This project is a a predictive algorithm used to predict the salary of someone with the given attributes about themselves, the outcome will predict whether or not you'll make over, under or exactly 50k
We've all been at crossroads when it comes to what we want to pursue; however, our A.I. can provide users with a clear path. Our goal is to guide users to their future career based on what they wish to accomplish with their education.
The data set is a classification on salary that determines whether a person makes less than or equal to 50K or greater than 50K based on their personal attributes.
Classification refers to a binary set data, aka and off or on. Regression refers to data that is cannot be classified as binary, usually numerical or quantifiable data. Our set is classification because this AI categorizes the data to be either over 50k or under 50k.
A prediction site that provides users with information in regards to their salary. The data set shows the correlation between education, occupation, and salary and predicts whether someone’s salary will be more or less than 50k based on the given information.
We are the Electric Zombies, a group of six students attending an A.I. summer camp. One of our main projects in this camp is creating an A.I. model based on data sets. We decided to commit to a salary predictor as it can be helpful to those who may need a clear outcome towards their desired income based on their personal attributes such as occupation and education level.
Because real-world data typically contains too much noise and only a few columns that give useful information, it is recommended that these columns be removed before preforming any data analysis. For our data set, we removed columns that contained other sources of income besides the main occupation in order to ensure our data was accurate.
Real world data always comes with gaps in the data these are called null values. They can be treated in many ways however, one of the most widely used methods (and the one we used ourselves) is to impute the null values with the mean, median, mode or nearby values.
Since new world data contains both numerical and categorical data, these categorical columns are required to be encoded. When fed to a machine learning model, as machine learning can only understand numeric data, these categorical data values are encoded to zeros and ones. Hence, making them more recognizable to machines.

Feature engineering is the process of selecting, manipulating, and transforming raw data into features that can be used in supervised learning. With the help of data validation, we can improve the the accuracy and quality of the source data.

The train-test split is used to estimate the performance of machine learning algorithms that are applicable for prediction-based Algorithms/Applications. We use training data to train the machine learning model and test data to evaluate the performance of the model.

Since real world data contains both numerical and categorical data, these categorical columns are required to be encoded. when fed to a machine learning model, as machine learning can only understand numeric data, these inserted values are encoded to zeros and ones.

For machine learning, we used three models; Logistic Regression, Random Forest and Neural Network. These models are used for classification of the sample data. After testing each model we found that Neural Network provided the highest accuracy result with 84%.
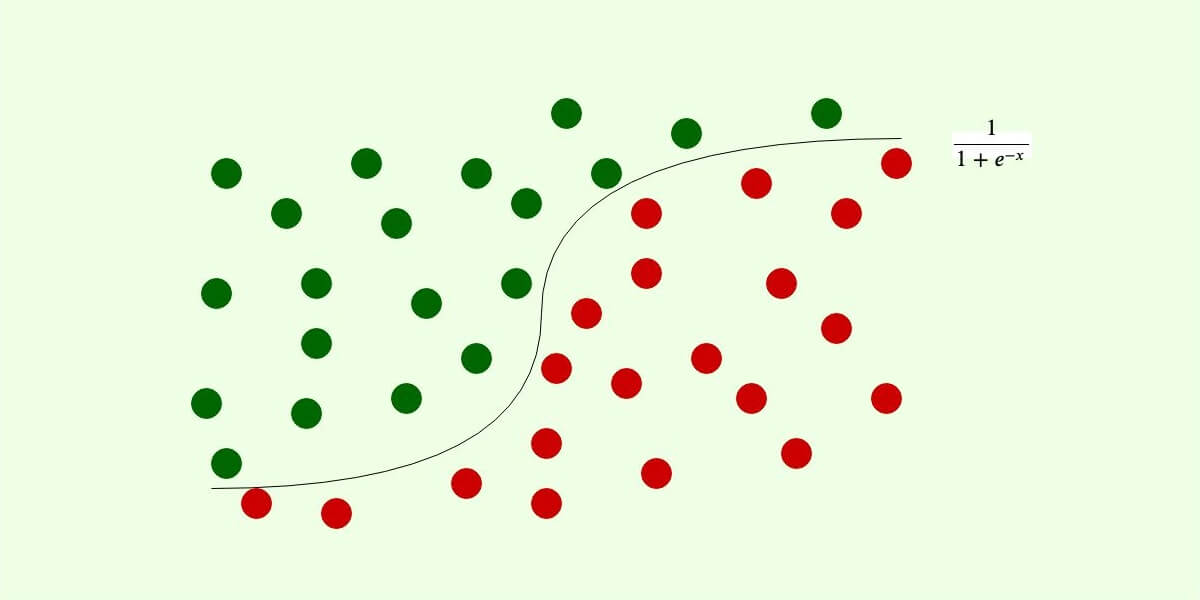
Logistic regression is a method used to predict a binary outcome, such as yes or no, based on prior observations of a data set. A Logistic Regression model predicts a dependent data variable by analyzing the relationship between one or more existing variables. In Logistic Regression, an "S" shaped logistic function is used to predict two maximum values (0 or 1). The curve from the Logistic Regression function indicates the likelihood of the occurrence of each data piece.
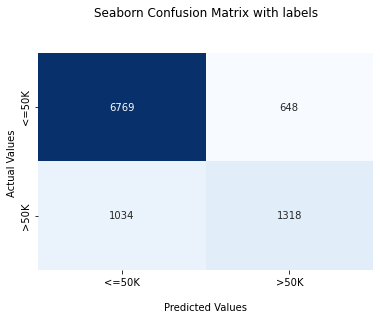
Confusion Matrix for Logistic Regression:
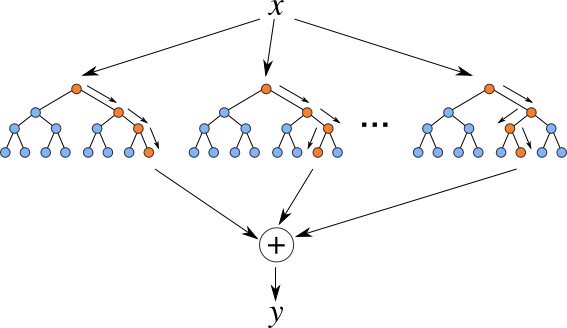
Random Forests are a sequence of decision trees, that perform classification or regression by asking true or false questions which get solved with a majority vote. Each tree makes a class prediction, and the prediction with the most votes becomes our model's final prediction.By using uncorrelated trees who give individual outputs, the Random Forest model generates a prediction by the committee that is more accurate than that of any individual tree.
Confusion Matrix for Random Forests:

A neural network is a method in artificial intelligence that teaches computers to process data in a way that is inspired by the human brain. It is a type of machine learning process, called deep learning, that uses interconnected nodes or neurons in a layered structure that resembles the human brain. Some projects that have used Neural Networking that are used in a day to day basis are weather forecasting, credit scoring websites, and fraud detection systems.
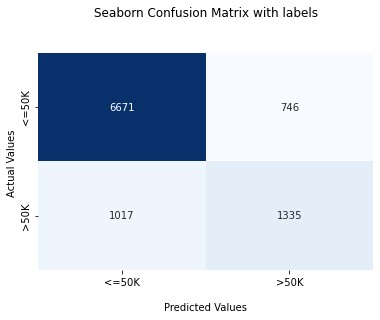
Confusion Matrix for Neural Networks:
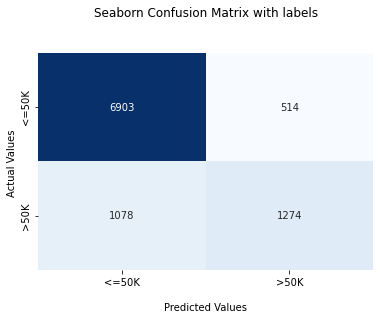
Confusion Matrix is a performance measurement for the machine learning classification problems where the output can be two or more classes. It is a table with combinations of predicted and actual values.
| Predicted: 0 | Predicted: 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Actual: 0 | True Negative (TN) | False Positive (FP) |
| Actual: 1 | False Negative (FN) | True Positive (TP) |
Accuracy is one metric for evaluating classification models. Informally, accuracy is the fraction of predictions our model got right.Accuracy is a good measure when there is class balance i.e. when both classes are almost equal or comparable. For imbalance classes other metrics such as precision , recall etc will give better perception on how model is performing on new data.
Accuracy = \(\frac {TP+TN}{TP+TN+FP+FN}\)
Recall explains how many of the actual positive cases we were able to predict correctly with our model. It is a useful metric in cases where False Negative is of higher concern than False Positive. It is important in medical cases where it does not matter whether we raise a false alarm but the actual positive cases should not go undetected!
Recall = \(\frac {TP}{TP+FN}\)
Precision explains how many of the correctly predicted cases actually turned out to be positive. Precision is useful in the cases where False Positive is a higher concern than False Negatives. The importance of Precision is in music or video recommendation systems, e-commerce websites, etc. where wrong results could lead to customer churn and this could be harmful to the business.
Precision = \(\frac {TP}{TP+FP}\)
The F1-score (also sometimes called the F-Measure) is a single performance metric that takes both precision and recall into account. It's calculated by taking the harmonic mean of the two metrics.Only when both precision and recall have good performance will the F1-score be high.
F1 Score = \(\frac {2 . Precision . Recall}{Precision + Recall}\)
After analyzing our data, we found that out of all of the classification models, Neural Networks worked the best for predicting salary. Our Logistic Regression and Random Forest models both had an accuracy of around 82%, while our Neural Network model had an accuracy of around 84%, making it the best of the three that we used. From the analysis we can conclude that there is a relation between level of education, age, race etc.. and income received by a person.
Experimenting until I find what works

The best way to predict the future is to create it

Winner of the worst wifi award

Model Analyst || Backend Developer || Musician

I did my best and that’s all that matters

Team Member

Instructor
You Will Never Walk Alone